- qPCR's rapid, accurate and sensitive results give a comprehensive understanding of microbial populations, which is crucial for monitoring fermentation progress, detecting spoilage organisms, and ensuring product stability.
- Providing real-time insights into kinetics and microbial dynamics, qPCR can monitor yeast and bacterial populations during fermentation,
- During aging, qPCR is invaluable for monitoring microbial activities, such as the growth or presence of lactic acid bacteria or Brettanomyces.
Quality assurance in wine-making
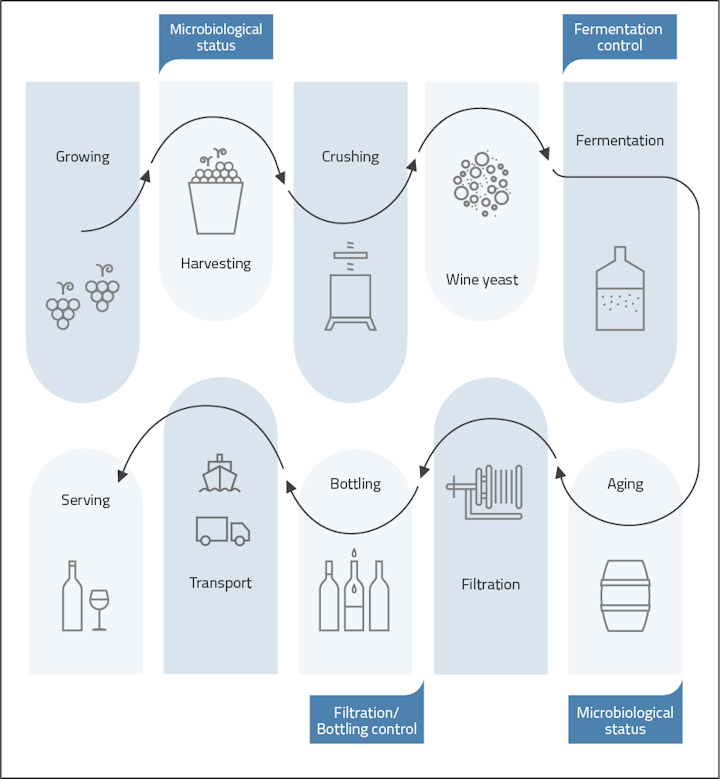
qPCR has emerged as a supporting tool for quality assurance throughout the wine-making process, providing winemakers and bottling companies with rapid and accurate methods for assessing microbial populations, detecting spoilage organisms, and ensuring product consistency.
It allows rapid and accurate detection of microorganisms, such as specific spoilage yeast and bacteria, throughout the winemaking process. This enables winemakers to identify potential issues early on and take corrective actions to maintain product quality.
Moreover, qPCR is highly sensitive and can detect microorganisms even at low levels, providing a comprehensive understanding of microbial populations in the wine or must. This sensitivity is crucial for monitoring fermentation progress, detecting spoilage organisms, and ensuring product stability.
Expanding the qPCR toolkit:
Monitoring Fermentation and Aging Processes
During fermentation, qPCR can be used to monitor yeast and bacterial populations, providing real-time insights into fermentation kinetics and microbial dynamics. This allows winemakers to optimize fermentation conditions, troubleshoot issues such as sluggish fermentations, and ensure the desired flavor profile of the final product.
During aging, qPCR is invaluable for monitoring microbial activities such as the growth or presence of lactic acid bacteria or Brettanomyces (Dekkera). qPCR can be used in two ways: to ensure no malolactic fermentation (MLF) takes place or to ensure the desired lactic acid bacteria population is growing and MLF is being conducted and completed.
Brettanomyces contamination poses a significant threat to wine quality, as even low levels of these yeast species can result in undesirable sensory characteristics, such as earthy, barnyard, or medicinal aromas. Traditional methods for detecting Brettanomyces, such as plating techniques, are time-consuming and may not provide the sensitivity required to detect low-level contamination. This is where qPCR steps in, offering rapid and sensitive detection of Brettanomyces DNA, even at levels below sensory thresholds.
Post-filtration assurance: Ensuring yeast-free wines
Even after filtration, the risk of yeast contamination remains a concern for winemakers. Second fermentations can take place in the bottle and end in bottle explosions in the worst case. qPCR provides a reliable and fast method for verifying the absence of yeast in the finished wine, offering peace of mind and ensuring product stability during storage and distribution.
Overall, qPCR's speed, sensitivity, specificity, and quantification capabilities make it a beneficial tool contributing to the HAPPC concept. By integrating qPCR into their quality control protocols, winemakers and bottlers can enhance product quality, minimize spoilage risks, and ensure consumer satisfaction and safety.
Products of potential interest:
Microbial status:
Must and Fermentation
GEN-IAL® QuickGEN Wine Screening low MG
GEN-IAL® QuickGEN Yeast differentiation low
GEN-IAL® QuickGEN Wild yeast 2 low
Aging:
GEN-IAL® QuickGEN Dekkera bruxellensis quantitative low
QuickGEN PCR Kit Oenococcus oeni -low
Bottling:
QuickGEN PCR Kit Yeast universal -low
Contact us for further information or a demo on-site. Use the Request Information button below to connect with us directly.