Introduction
NEMIS Technologies presents a detailed field study at a sushi production facility to evaluate the real-world performance of the N-Light™ Listeria monocytogenes test. Unlike competitors who often rely on laboratory settings for testing, NEMIS chose to test in the actual food production environment, showcasing a commitment to real-world accuracy and reliability.
Study design
The study involved collecting 90 samples over two days using the N-Light™ Neutralizer for sample collection. A diverse range of samples was collected within the sushi production areas to comprehensively assess the environment and the test's effectiveness in various facility zones. To address the naturally low prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes, the study included a spiking step using chilled-stressed Listeria.
Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19111 was grown and incubated on non-selective agar at 37 °C for the bacterial inoculum for 18-24 hours. A single colony from this culture was set in BHI broth under the same conditions. After incubation, the culture was chilled at 4 °C for 72 hours. The bacteria were then plated, diluted, and used to spike the samples with 200 cfu/ml of the chill-stressed Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19111, ensuring all samples were uniformly positive for L. monocytogenes.
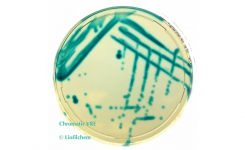
Each sample was tested using the N-Light™ L. monocytogenes test and the ISO 11290-1 method. This allowed for a comprehensive comparison between the rapid N-Light™ test and the established ISO method for detecting Listeria monocytogenes. The final step involved a confirmation process from the N-Light™ L. monocytogenes test, where the tube contents were directly inoculated on Agar Listeria according to Ottaviani and Agosti and incubated at 37 °C for 48 hours. This systematic approach aimed to validate the rapid test's accuracy compared to the standard industry method.

Result
Swabs were taken from critical points identified in the producer's HACCP study, covering all hygiene zones from the high-risk zone 1 to the low-risk zone 4. The test showed excellent performance within its recommended usage, achieving over 93% sensitivity, closely matching the ISO reference method.
The overall impressive sensitivity of 93% can be further enhanced in practical applications by avoiding factors that decrease performance, such as overloading the sample with food matrix residues from the production line or equipment and old dirt from hard-to-reach areas.
A key observation from the study was the lack of correlation between test performance and the hygiene zone of testing. This indicates that the test consistently maintained its sensitivity across different locations within the sushi production facility.
Furthermore, the study found that using direct confirmation from the tube on an ALOA plate was highly influential, demonstrating 100% sensitivity. These findings support using simple ALOA plating as a reliable and rapid confirmation method, eliminating the need for the more lengthy and expensive full ISO cultural method.


Conclusion
The field study conducted by NEMIS in the ready-to-eat (RTE) factory, assessing the N-Light™ Listeria monocytogenes test, showcased outstanding performance. With an impressive sensitivity rate of 93%, the test's efficacy can be further enhanced by careful sample collection, avoiding contamination with food residues or accumulated dirt. The N-Light™ L. monocytogenes test stands out for its user-friendliness, ability to be used outside of lab settings, and capacity to deliver actionable results within a 24-hour. This makes it an invaluable tool for risk mitigation and maintaining control in any ready-to-eat food production facility.
Visit NEMIS for more, or use the Request Information button to connect directly with the supplier.